Above picture we shown current chart is EURUSD and indicator shown another line chart for EURNZD(need to putted).
Above picture we shown current chart is EURUSD and indicator shown another line chart for EURNZD(need to putted).
 Within a same chart when we can see two pairs line then we can speculate the future movement of this two pair by using the currency correlationship method.
Indicator is here
It is the property of this site
Download from here
v2.88_fxr_correlation
Within a same chart when we can see two pairs line then we can speculate the future movement of this two pair by using the currency correlationship method.
Indicator is here
It is the property of this site
Download from here
v2.88_fxr_correlation Understanding Forex Currency Correlation
Forex currency pairs exhibit various types of correlations: positive, negative, or zero. Understanding these correlations is crucial for effective trading strategies.
What is Correlation?
Positive Correlation
A positive correlation means that two currency pairs tend to move in the same direction. For instance, when the market is bullish, both pairs will generally rise together. Conversely, during bearish trends, both pairs will decline simultaneously. This characteristic makes them mirror reflections of one another.
Negative Correlation
In contrast, a negative correlation indicates that one currency pair moves in an opposite direction to another. If one pair rises, the other tends to fall, resulting in potential losses if both pairs are traded simultaneously.
Zero Correlation
Zero correlation means there is no predictable relationship between the movements of the two currency pairs. Their price movements are independent of each other.
Importance of Correlation in Forex Trading
Understanding currency correlation is critical for several reasons:
Risk Management
Knowing the correlation between trades helps plan lot sizing effectively. For example, trading two negatively correlated pairs may lead to zero net gain, as profits from one might cancel losses from the other.
Overtrading Prevention
Engaging in trades with positively correlated pairs can lead to increased risk exposure, effectively doubling your investment in a similar market trend. This strategy can be detrimental if the market moves against your positions.
The Correlation Indicator
The correlation indicator is a useful tool in forex trading. It overlays the price movement of a second currency pair onto the existing chart, allowing for real-time observation of their relationship.
How the Correlation Indicator Works
While it does not provide direct buy or sell signals, the correlation indicator helps traders visualize the price movements of two correlated currency pairs side-by-side. This enables traders to analyze market behavior over time, candle by candle.
Using the Correlation Indicator for Trading
Identifying Trading Opportunities
Correlations are valuable for pinpointing potential market turning points. If two positively correlated currencies display a divergence in their trends, that presents an opportunity to enter a trade.
– Example:
If the EUR/USD shows a sharp decline while the GBP/USD is less affected, this disparity can signal a buying opportunity in GBP/USD, expecting a correction.
Real-World Trading Scenario
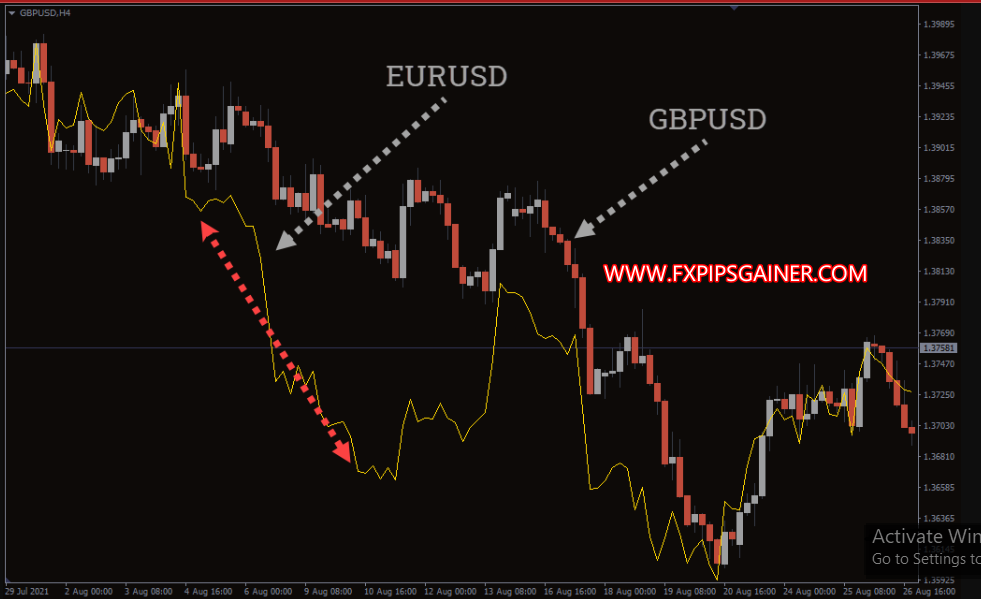
– Currency Pairs:
EUR/USD and GBP/USD
– Observation:
The price chart depicts EUR/USD with a sharp decline (red arrows), while GBP/USD also trends downward but less steeply.
In this instance, given their positive correlation, traders would anticipate a future decline in GBP/USD once it aligns more closely to the EUR/USD trend.
How to Trade with the Correlation Indicator
Trading with the correlation indicator involves identifying opportunities based on the correlation between currency pairs. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to do it effectively.
1. Set Up the Correlation Indicator
– Install the Indicator:
Add the correlation indicator to your trading platform (e.g., MT4).
– Select Pairs:
Choose the currency pairs you want to analyze, focusing on those with known correlations.
2. Analyze Correlation Relationships
– Identify Positive Correlations:
Look for pairs that move in the same direction. For example, EUR/USD and GBP/USD typically show positive correlation.
-Identify Negative Correlations:
Observe pairs that move in opposite directions, like USD/JPY and EUR/USD.
3. Look for Divergence Opportunities
– Trend Disparity:
Monitor the charts for occasions when positively correlated pairs start diverging. This signals a potential trading opportunity.
– Example:
If EUR/USD declines sharply but GBP/USD remains stable or rises, it could indicate a trading opportunity.
4.Determinate Entry Points
– Entry Signal:
Enter a trade on the pair that is lagging, expecting it to align with the stronger trend of the correlated pair.
– Confirmation:
Use additional indicators or candlestick patterns to confirm your entry signal.
5. Set Stop Loss Levels
– Identify Stop Loss Placement:
– For buy trades, place your stop loss below the recent swing low.
– For sell trades, position it above the recent swing high.
– Risk Management: Ensure that the stop loss reflects a risk-reward ratio you are comfortable with (e.g., 1:2).
6. Set Take Profit Levels
-Determine Take Profit Target:
– Use support and resistance levels from the price action of the correlated pairs.
– Aim for a profit level that reflects a realistic target based on the volatility of the currency pair.
– Adjust Targets:
Be flexible and adjust take profit levels based on market conditions and new information.
7. Monitor and Adjust Trades
– Track Correlation:
Continuously monitor the correlation to see if it strengthens or weakens throughout the trade.
-Adjust Stop Loss and Take Profit:
If the market moves favorably, consider trailing your stop loss to lock in profits.
8. Exit the Trade
– Finalize Position:
Exit the trade when your take profit is hit or when the market reverses against your position (hit stop loss).
– Review and Learn:
After the trade, analyze the outcome. Identify what worked and what didn’t for future improvements.
By following these steps, traders can effectively utilize the correlation indicator to capitalize on forex market opportunities.