Maximize your profit by copy our Trade
In the forex market, an order refers to the specific instructions a trader provides to their broker to open or close a trade. Essentially, an order outlines the conditions under which a trader wants to enter or exit a currency position.
The various order types available in the forex market allow traders to tailor their trading strategies and manage risk more effectively. Some of the key order types include:
1.Market Orders
2.Limit Orders
3.Stop Orders
4.Stop-Limit Orders
5.Trailing Stop Orders
1.Market Orders and
2. Pending Orders
Limit Order
-Buy Limit
-Sell Limit
Stop Order
-Buy Stop
-Sell Stop
1.Market Orders:
A market order is an instruction to buy or sell a currency pair at the best available price in the current market.
For example, if the current bid price for EUR/USD is 1.2140 and the ask price is 1.2142, a market order to buy EUR/USD would be executed at the ask price of 1.2142.
The key points about market orders are:
They are executed immediately at the best available price in the market.
The final execution price may differ slightly from the quoted price at the time of order placement due to market volatility.
Market orders provide the fastest way to enter or exit a position, but traders sacrifice some control over the exact entry/exit price.
This immediacy and lack of price control is the tradeoff with market orders. Traders use them when speed of execution is the priority over getting a specific target price.
Now, let’s move on to the different types of pending orders in the forex market.
2.Pending Orders:
-Buy Limit Order
-Sell Limit Order
-Buy Stop Order
-Sell Stop Order
Limit Orders
Limit orders allow traders to specify the exact price at which they want to enter or exit a trade. There are two main types of limit orders:
Buy Limit Order:
A buy limit order is placed to purchase a currency pair at a price lower than the current market price. The order will only be executed if the market price reaches the specified limit price or better. For example, if the current EUR/USD price is 1.2050, you could place a buy limit order at 1.2040 to enter a long position if the price drops to that level.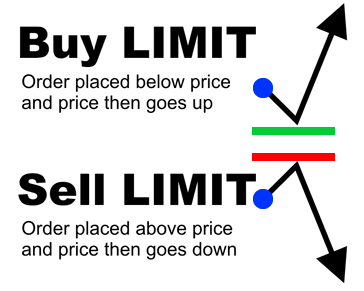
Sell Limit Order:
A sell limit order is used to sell a currency pair at a price higher than the current market price. The order will only be executed if the market price reaches the specified limit price or higher. For example, if the current EUR/USD price is 1.2050, you could place a sell limit order at 1.2060 to enter a short position if the price rises to that level.
The key benefit of limit orders is that they allow traders to take advantage of favorable price levels, while avoiding unfavorable ones. Limit orders can only be executed at the specified price or better, giving traders more control over their entry and exit points compared to market orders.
Maximize your profit by copy our Trade
Stop Entry Orders
Stop entry orders are instructions to buy or sell a currency pair once the market price reaches a specific level, known as the stop price. There are two main types of stop entry orders:
Buy Stop Order:
A buy stop order is placed above the current market price. It is triggered and executed when the market price rises to the specified stop price or higher. For example, if the current EUR/USD price is 1.2050, you could place a buy stop order at 1.2060 to enter a long position if the price rises to that level.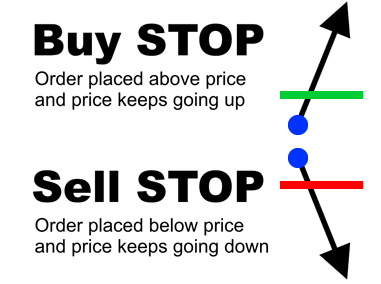
Sell Stop Order:
A sell stop order is placed below the current market price. It is triggered and executed when the market price falls to the specified stop price or lower. For example, if the current EUR/USD price is 1.2050, you could place a sell stop order at 1.2040 to enter a short position if the price drops to that level.
The key benefit of stop entry orders is that they allow traders to automatically enter a new position once the market reaches a specific price level. This can be useful for traders who want to take advantage of a potential breakout or trend continuation, but do not want to constantly monitor the market.
For instance, using the example above, if you believe that GBP/USD will continue to rise after reaching 1.5060, you can place a buy stop order at that level instead of manually executing the trade when the price hits that point. This allows you to enter the position automatically without having to watch the market constantly.
Stop Loss Orders
A stop loss order is a type of order that is used to limit the potential loss on an open position. It is an order to buy or sell a currency pair once the market price reaches a specific level, known as the stop price.
When you have an open long position (a buy order), the stop loss order is a sell order that is placed below the current market price. If the market price falls to the stop price or below, the stop loss order is triggered and executed, closing the long position and limiting your potential losses.
Conversely, when you have an open short position (a sell order), the stop loss order is a buy order that is placed above the current market price. If the market price rises to the stop price or above, the stop loss order is triggered and executed, closing the short position and limiting your potential losses.
For example, let’s say you opened a long position on EUR/USD at 1.2230. To limit your potential loss, you could set a stop loss order at 1.2200. This means that if the market price falls to 1.2200 or below, your trading platform will automatically execute a sell order at the best available price, closing your long position and limiting your loss to 30 pips.
Stop loss orders are an essential risk management tool for forex traders. They help you define your maximum acceptable loss on a trade, allowing you to stay in the market without the constant fear of losing your entire account balance. By using stop loss orders, you can focus on your trading strategy and let the market move without worrying about catastrophic losses.
Stop orders may not execute at the specified price, especially in volatile markets. A sell stop can trigger below the stop price, and a buy stop above it, potentially leading to undesirable executions.
Trailing Stop
A trailing stop is a type of stop loss order that automatically adjusts to lock in profits as the market moves in the trader’s favor. The stop loss follows or “trails” the market price, maintaining a fixed distance from the current market price.
Here’s how a trailing stop works:
Example:
Let’s say you’ve decided to short USD/JPY at 90.80, with a trailing stop of 20 pips.
1.Initial Stop Loss: Your original stop loss would be set at 91.00 (20 pips above your entry price of 90.80).
2. Trailing Stop Moves with Profit: As the price of USD/JPY drops, your trailing stop will move down accordingly. For example, if the price falls to 90.60, your trailing stop will move down to 90.80 (breakeven).
3.Locking in Profits: If the price continues to decline and reaches 90.40, your trailing stop will move down to 90.60, locking in a 20 pip profit.
4. Closing the Position: Your trade will remain open as long as the price does not move against you by 20 pips (the distance of your trailing stop). Once the market price hits your trailing stop price of 90.60, a market order will be sent to close your position at the best available price.
The key advantage of a trailing stop is that it allows you to protect your profits as the market moves in your favor, while still limiting your downside risk. The stop loss level automatically adjusts to trail the current market price, ensuring that you can capture gains without giving them back.
It’s important to note that the trailing stop will not widen if the market moves against you. It will only move in the direction of your profitable trade, locking in gains incrementally as the price fluctuates.
Limit Orders versus Stop Orders
Limit orders and stop orders are both common order types used in financial trading, but they serve different purposes. The key difference lies in the purpose of the specified price.
Limit Orders
A limit order allows you to specify the maximum or minimum price at which you are willing to buy or sell a financial instrument. The order can only be executed at the limit price or better.
Example:
Suppose the current market price of EUR/USD is 1.1000. You want to buy EUR/USD, but you don’t want to pay more than 1.1009. You can place a limit buy order at 1.1009. This order will only be executed if the market price reaches 1.1009 or lower, ensuring you get the price you want or better.
The advantage of a limit order is that it guarantees the price at which your order will be filled. However, the trade-off is that your order may not be executed if the market price never reaches your specified limit price.
Stop Orders
In contrast, a stop order is designed to limit losses or protect profits. It is triggered when the market price reaches or passes a specified stop price, at which point it becomes a market order.
Example:
Let’s say the current market price of EUR/USD is 1.1000, and you have a short position. You want to limit your downside risk, so you place a stop buy order at 1.1010. If the market price rises to 1.1010 or higher, your stop order will be triggered, and your position will be closed at the best available market price.
The key difference is that a stop order does not guarantee the exact price at which your order will be filled. The order will be executed at the best available market price once the stop price is reached, which may be better or worse than the specified stop price, depending on market conditions.
In summary, limit orders allow you to specify the exact price at which you are willing to trade, while stop orders activate a market order when a specified price level is reached, with the actual execution price depending on market conditions at the time.
Maximize your profit by copy our trade
Weird Forex Orders
Good ‘Till Cancelled (GTC)
A GTC order remains active in the market until you decide to cancel it. Your broker will not cancel the order at any time. Therefore, it is your responsibility to remember that you have the order scheduled.
Good for the Day (GFD)
A GFD order remains active in the market until the end of the trading day. Because foreign exchange is a 24-hour market, this usually means 5:00 pm EST since that’s the time U.S. markets close, but we’d recommend you double-check with your broker.
GFD and GTC are known as “time in force” orders. The “time in force” or TIF for an order defines the length of time over which an order will continue working before it is canceled. Think of it as a special instruction used when placing a trade to indicate how long an order will remain active before it is executed or expires.
One-Cancels-the-Other (OCO)
An OCO order is a combination of two entry and/or stop loss orders. Two orders are placed above and below the current price. When one of the orders is executed, the other order is canceled.
An OCO order allows you to place two orders at the same time. But only one of the two will be executed. For example, if the price of EUR/USD is 1.2040, you want to either buy at 1.2095 over the resistance level in anticipation of a breakout or initiate a selling position if the price falls below 1.1985. The understanding is that if 1.2095 is reached, your buy order will be triggered and the 1.1985 sell order will be automatically canceled.
One-Triggers-the-Other (OTO)
An OTO is the opposite of the OCO, as it only puts on orders when the parent order is triggered. You set an OTO order when you want to set profit-taking and stop loss levels ahead of time, even before you get in a trade.
For example, if USD/CHF is currently trading at 1.2000, you believe that once it hits 1.2100, it will reverse and head downwards but only up to 1.1900. You can set a sell limit at 1.2100 and at the same time, place a related buy limit at 1.1900, and a stop-loss at 1.2130. As an OTO, both the buy limit and the stop-loss orders will only be placed if your initial sell order at 1.2000 gets triggered.
An OTO and OTC order are known as conditional orders, where an order includes one or more specified criteria.
Trade Now
Conclusion
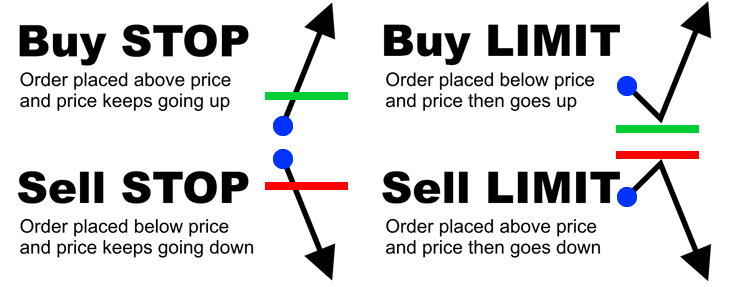
In conclusion, the basic forex order types such as market, limit entry, stop entry, stop loss, and trailing stop are usually all that most traders ever need. To open a position, the following pending orders may be used:
– “Buy stop” to open a long position at the price higher than the current price
– “Sell stop” to open a short position at the price lower than the current price
– “Buy Limit” to open a long position at the price lower than the current price
– “Sell Limit” to open a short position at the price higher than the current price
While the more complex order types like Good ‘Till Cancelled (GTC), Good for the Day (GFD), One-Cancels-the-Other (OCO), and One-Triggers-the-Other (OTO) can be useful in certain situations, the core set of basic order types are typically sufficient for most forex trading needs.

