Maximize your profit by copy our Trade
Understanding Imbalance and Fair Value Gaps (FVG)
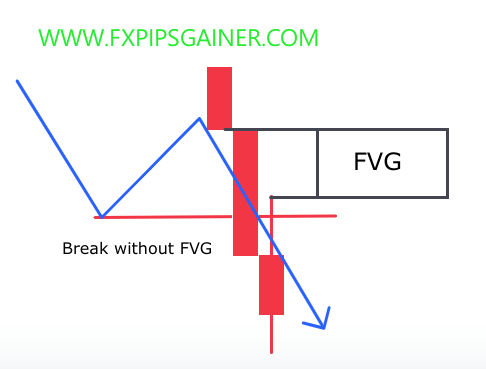
Imbalance, often referred to as a Fair Value Gap (FVG), is a concept used in trading, particularly within the context of the Smart Money Concept (SMC). It represents areas on a price chart where the market has moved rapidly, leaving behind a gap that has not been filled by subsequent price action. This phenomenon occurs due to significant buying or selling pressure from large market participants, such as banks and institutional investors, leading to sharp price movements.
Key Characteristics of Imbalance
- Formation: Imbalances typically consist of three candles:
- Identification:
- Liquidity Consideration: Imbalances are often considered stronger if they follow a liquidity sweep, meaning that the price has previously collected liquidity above recent highs or below recent lows before the imbalance forms.

Importance of Imbalance in Trading
- Market Sentiment: Imbalances can give insight into the sentiment of large market participants.
- Price Movement: Prices often return to fill these gaps, making them potential areas for future price action.

Analyzing Imbalance for Trade Decisions
- Identify Recent Price Action: Look for rapid movements in price that create gaps between candles.
- Mark Imbalances: Identify the three-candle structure and mark the boundaries of the imbalance.
- Assess Liquidity: Consider whether the imbalance followed a liquidity sweep.
- Monitor for Price Reaction: Watch how the price interacts with the identified imbalance in future sessions.
Rules for Long Entries in Trading
There are two primary options for entering long trades:
- On the Trend’s Reversal
- After a Correction of the Trend
Both options can be effective, but they have minor differences in execution. Trend reversals can be more challenging to capture because the market often continues in the direction of the prevailing trend.
Long Entry on Trend Correction
This section focuses on entering long trades during trend corrections. Follow these steps:
- Wait for Strong Momentum: Observe the price moving higher with strong momentum, resulting in the formation of a Fair Value Gap (FVG).
- Liquidity Pool Collection: It’s advantageous if the price collects a liquidity pool before making a further upward move.
- Enter the Trade: Wait for the price to retrace into the FVG. This is your entry point for opening a long trade.
- Set Stop Loss: Place your Stop Loss below the last swing low to protect your trade from unexpected market moves.
- Set Take Profit: Target a Take Profit level above the recent high to maximize your potential gains.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Ensure that you maintain a decent risk-reward (RR) ratio. A ratio of 1:3 is often considered ideal. If the potential reward is lower, it may be wiser to skip the trade.
Example of a Long Trade
In the above example, we open a trade in the middle of the FVG as indicated in the upper chart to achieve a 1:3 RR ratio. This setup illustrates the effectiveness of entering during a trend correction, capitalizing on the momentum and the established gap.
Rules for Short Entries in Trading
There are two primary options for entering short trades:
- On the Trend’s Reversal
- After a Correction of the Trend
Both options can be effective, but they have minor differences in execution. Trend reversals can be more challenging to capture because the market often continues in the direction of the prevailing trend.
Short Entry on Trend Correction
Follow these steps to enter a short trade during a trend correction:
- Wait for Liquidity Sweep: Monitor the price for a sweep of the closest liquidity pool, which should precede a reversal.
- Formation of FVG: Ensure that the price leaves a Fair Value Gap (FVG) behind as it reverses.
- Enter the Trade: Wait for the price to reach the FVG. You can enter the trade as soon as the price touches the imbalance or wait for it to fill the entire gap, depending on your risk management strategy.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Ensure your risk-reward (RR) ratio is at least 1:3 before entering the trade. If it is lower, consider skipping the entry.
- Set Stop Loss: Place your Stop Loss above the recent high to manage risk effectively.
- Set Take Profit: Target your Take Profit near the liquidity pool or at the lower end of the FVG, as these are likely price magnets.
Recent Posts
- Finding Your Path: How to Choose the Perfect Forex Mentor for Success
- Experience the Stability of a 100% Secure Trading Account!
- The 100% Profitable Trading Approach: Maximize Gains with Minimal Risk
- The Head and Shoulders Chart Pattern
- Bullish and Bearish Rejection Blocks: Identifying Key Trading Opportunities
- Just Market: Is It Worth Your Time and Money?
- Why LiteFinance Stands Out: A Comprehensive Review
- Understanding XAUUSD: Gold Strategy and Central Bank Reserve Management
- Hotforex Copy Trading Service
- Understanding Profit Factor: A Key Metric for Trading Success
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: How Gold Production Affects XAUUSD
- The Safe Haven: Gold as a Strategic Investment During Economic Downturns
- Mastering Deception: How to Scam as a Forex Signal Provider
- The Impact of Rising Bond Yields on Gold (XAUUSD)
- Understanding the Correlation Between Oil Prices and Gold (XAUUSD)
- The Impact of Geopolitical Events on Gold Demand (XAUUSD)
- Fundamental Strategy Overview: XAUUSD (Gold)
- Understanding the Role of Gold (XAUUSD) as an Inflation Hedge
- How Central Bank Interest Rates Influence Gold Demand
- Gold Holding Trading System
- From Novice to Pro: Navigating the ICT Propulsion Block in Trading
- Single Candle Order Block
- Is Scalping Right for You? Understanding the Advantages and Disadvantages
- The Dangers of Screenshot Trading: What You Need to Know
- Guidance for New Traders in Forex
- Forex Signal
- Understanding Market Psychology in Trading
- The Power of Order Blocks: Key Concepts Every Trader Should Know
- Understanding Imbalance and Fair Value Gaps (FVG)
- External and Internal Structure
- Causes of Market Pullbacks: What Every Investor Should Know
- Highs and Lows in Financial Markets: Key Concepts for Traders
- The Definitive Supply and Demand Trading Guide for Forex Traders
- Trading the Hanging Man with Pivot Points
- Trading the Hanging Man with Fibonacci Retracement
- Navigating Perfect Money: Pros and Cons You Need to Know
- Mastering the Super Signal Strategy with Donchian Channels
- Why Many Traders Lose in Forex: A Focus on Gold (XAU/USD)
- Beware of Forex Market Manipulation: Essential Insights for Traders
- Trading the Hanging Man with RSI Divergences
- The Forex Trader’s Blueprint: Understanding Supply and Demand Dynamics
- Trading the Hanging Man with Moving Averages
- Hanging Man Candlesticks Pattern
- Smart Money Concept(SMC) in Forex Market
- Advantages of Exness Forex Broker
- Trading the Hanging Man with Resistance Levels
- Bullish Harami Candlesticks Pattern
- Scalping Trading Strategy
- Trading with Confidence: A Closer Look at HFM Broker
- Swing Trading Strategy